Project Overview
This innovative project creates dementia-friendly urban spaces designed to enhance the quality of life for individuals with dementia and their caregivers. By incorporating wayfinding elements inspired by "lighthouses" and "buoys," the project establishes a memorable and accessible spatial network. Addressing the challenges posed by limited outdoor environments, this initiative promotes social interaction and physical activity among people with dementia.
Project Details
General Information
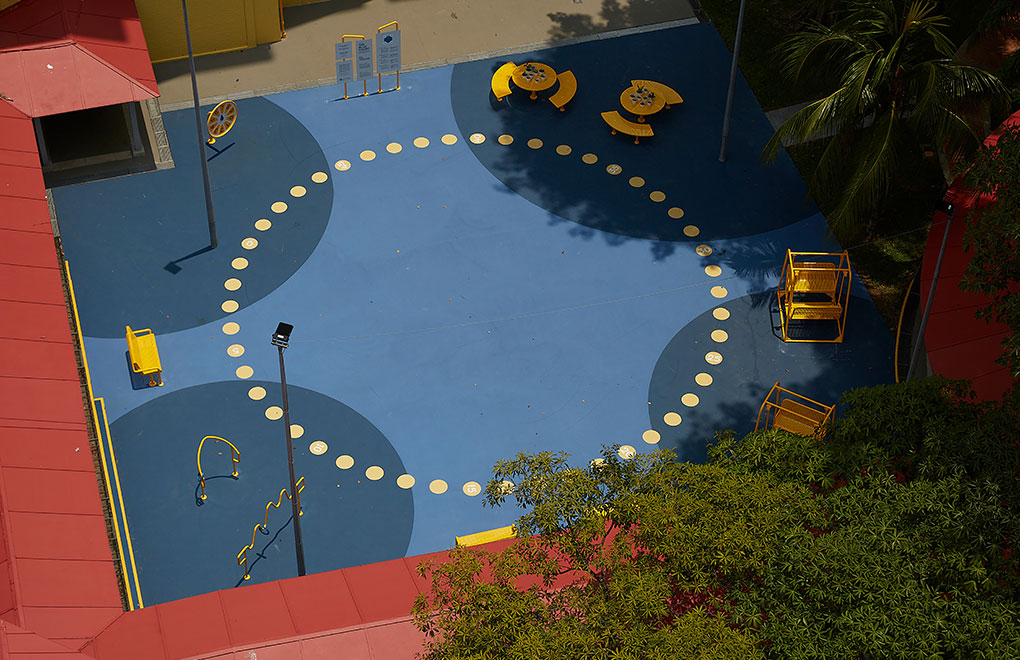
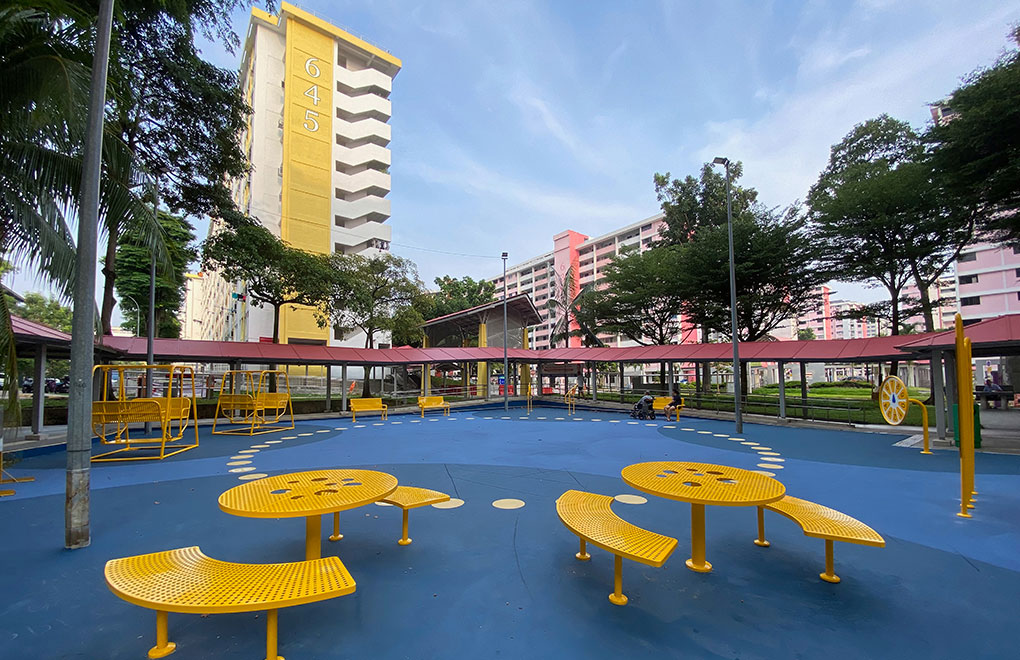
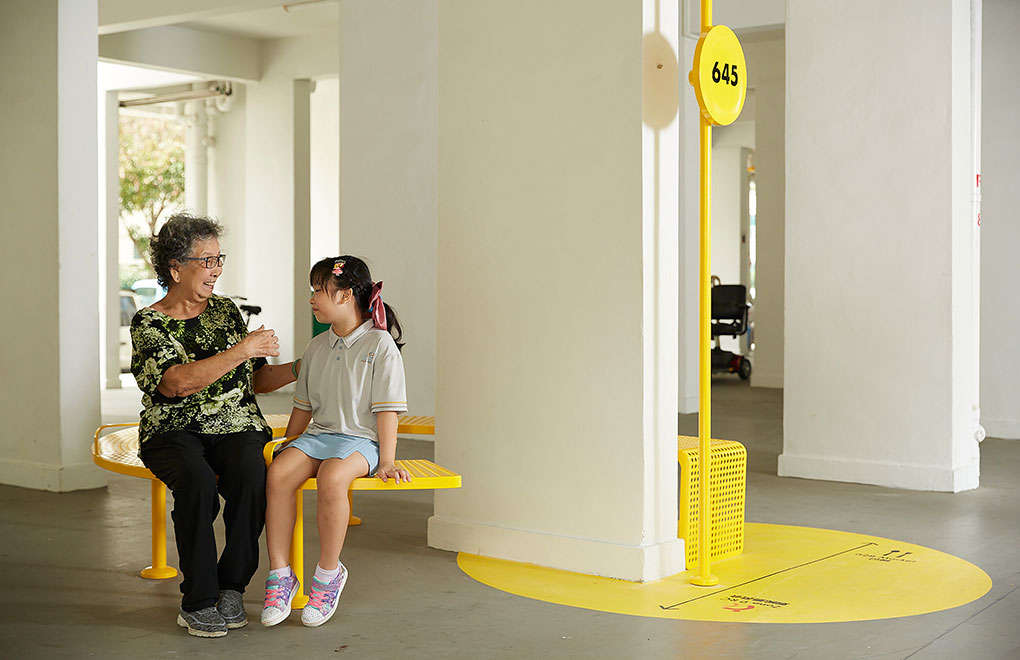
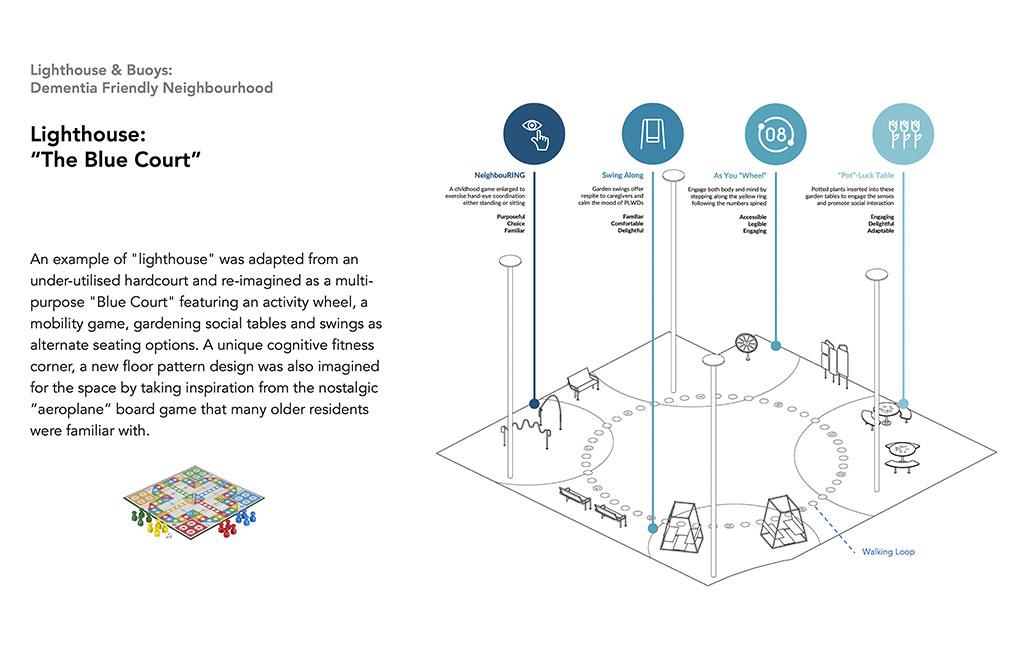
The Dementia-Friendly Neighbourhood project in Singapore addresses the critical need for outdoor environments conducive to people living with dementia (PLWDs). By employing a design-ethnographic approach, the project involved PLWDs and their caregivers to identify and address their unique needs. The resulting design interventions, guided by the principles: (+) strengthening mental maps, (-) minimalism, (x) community inclusion, and (%) incremental change, transformed key community locations into “lighthouses” and “buoys.” These interventions create a network of accessible, engaging, and memorable spaces that encourage PLWDs to venture outdoors, fostering social interaction and physical activity. The "Blue Court" and multi-generational games are examples of spaces that cater to both cognitive and physical well-being, promoting intergenerational bonding and community cohesion. By improving the navigability and inclusivity of neighbourhoods, the project enhances the quality of life for PLWDs, reduces caregiver burden, and fosters a supportive community. This sustainable approach not only aligns with Singapore's urban landscape but also promotes harmony between people, society, and the environment, creating a model for dementia- friendly urban design that can be replicated in other high-density cities.
Creative Solution (Creativity/Innovation)
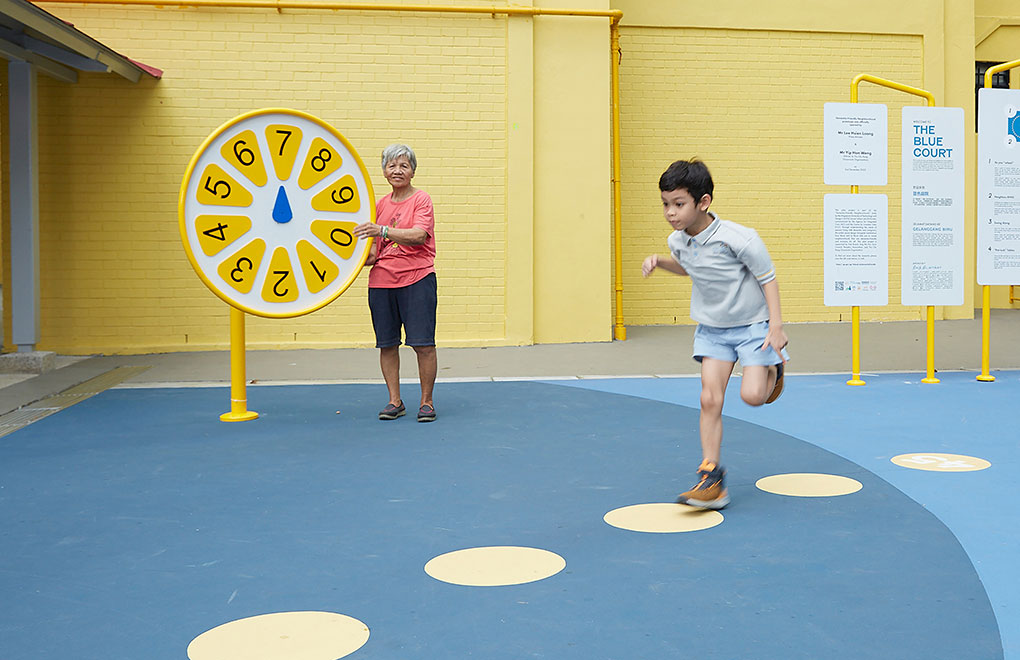
The Dementia-Friendly Neighbourhood project employs a creative, innovative approach by using design-ethnographic methodology (specially designed jigsaw moodboard and walking interview) to deeply understand the needs of PLWDs and their caregivers. Key interventions, inspired by the concepts of "lighthouses" and "buoys," create memorable, engaging, and accessible community spaces. These principles—(+) strengthening mental maps, (-) minimalism, (x) community inclusion, and (%) incremental change—transform the environment into a supportive, inclusive space. The "Blue CourtLighthouses" and "Buoys" exemplify innovative designs that promote cognitive and physical well-being, fostering intergenerational interaction and enhancing navigation.
Social Impact (Inspiration/Impact)
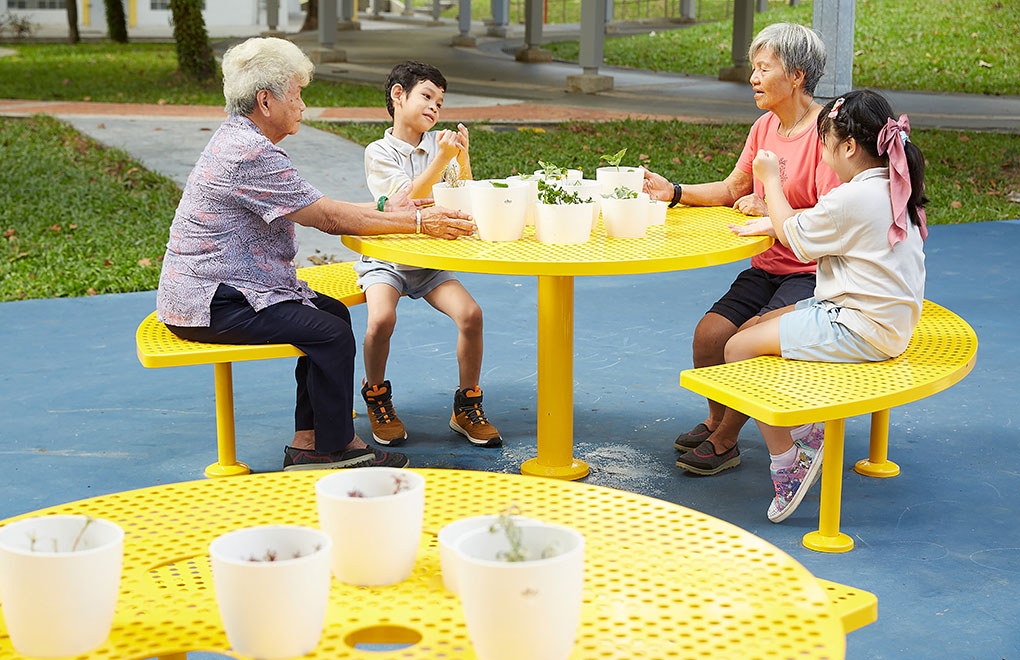
Our research findings highlighted that reducing the complexity of the spatial environment can improve PLWD's psycho- social perception of their neighbourhood and planning of PWLDs' favourite activities can encourage both PWLDs and their caregivers to leave their homes. This led to the 4 guiding design thinking principles, transforming key community nodes into "lighthouses" and "buoys," that provides clear navigation and promotes outdoor activity, social interaction, and mental stimulation. This approach not only enhances the quality of life for PLWDs and caregivers but also encourages intergenerational engagement. The project sets a precedent for sustainable urban design that prioritises inclusivity and community well-being.
Participation/Cooperation
We engaged various stakeholders in the development of the Dementia-Friendly Neighbourhood project, including ten pairs of PLWDs and their caregivers, who provided essential insights through participatory design methods. Community workshops involved 81 residents and local partners, fostering collaboration and ensuring the design interventions met local needs. Additionally, partnerships with organisations like Thye Hua Kwan Senior Activity Centre and Star Learners Preschool, along with support from Agency for Integrated Care (AIC) and Centre for Liveable Cities (CIC), facilitated the integration of health and social care perspectives, ensuring a comprehensive, community-driven approach to creating dementia-friendly environments.
Vision for the Future
The vision of the Dementia-Friendly Neighbourhood project is to create inclusive, engaging, and supportive environments that enhance the quality of life for people living with dementia (PLWDs) and their caregivers. By employing innovative design principles and fostering community collaboration, the project aims to transform urban spaces into dementia-friendly zones, especially in high-rise, high-density cities with hyper-sensorial outdoor environments. This forward-looking vision is scalable globally, offering a replicable model for cities worldwide to address the growing challenges of aging populations and promote sustainable, inclusive communities.